Main Idea:
Chest X-ray (CXR) images are the primary diagnostic tool in many healthcare centers due to their low cost and wide accessibility. However, their 2D limitations reduce accuracy in complex diagnoses. In this study, a novel approach is proposed for reconstructing 3D CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) images from CXR images using generative models and diffusion models in deep learning. Through cross-modality translation, this method reduces the need for expensive and high-risk imaging procedures, enhances diagnostic accuracy, and minimizes unnecessary CT scans. Evaluation results show that the generated images exhibit high anatomical accuracy, supporting the development of more accessible and cost-effective diagnostic tools. This approach is not only applicable to pulmonary imaging but also has the potential to be extended to other medical imaging applications, contributing to improved diagnostic quality and precision.
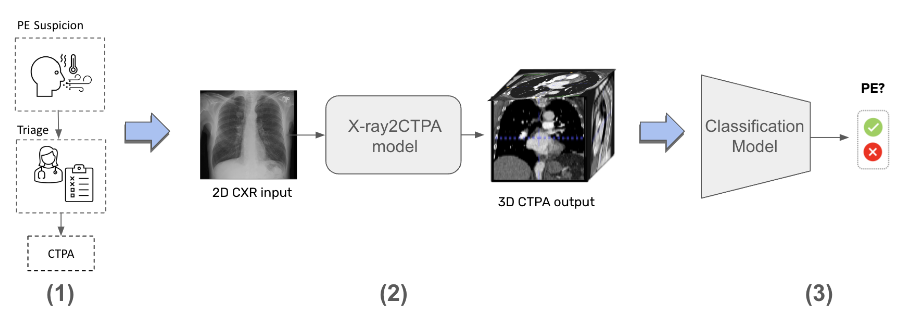
Explanation:
Medical imaging is one of the fundamental tools for diagnosing and monitoring pulmonary diseases. Currently, chest radiography (CXR) is among the most widely used imaging methods due to its low cost, high speed, and easy accessibility. However, its two-dimensional nature and low contrast limit its ability to reveal detailed structural information about the lungs, making it insufficient for accurate diagnosis of many pulmonary conditions. In contrast, CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA), as a three-dimensional imaging technique, provides detailed views of lung structures but comes with challenges such as high cost, the need for advanced equipment, and significant radiation exposure, limiting its widespread use.
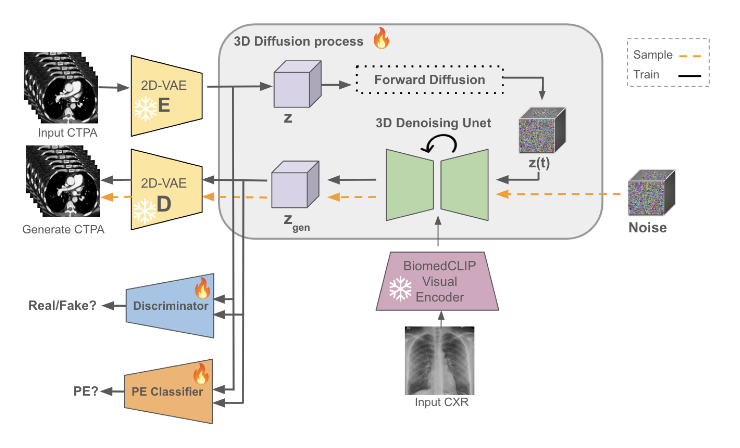
This study aims to introduce a novel method for reconstructing 3D CTPA images from 2D CXR images using generative models and diffusion models in deep learning. The developed model takes a chest X-ray as input and reconstructs the corresponding 3D anatomical structures, effectively enhancing the diagnostic value of standard 2D images. This approach not only improves the analysis and diagnosis of pulmonary diseases but also reduces the need for unnecessary CT scans and minimizes medical imaging costs.
An advanced AI architecture was employed in this project, trained on real CTPA and CXR datasets. The model is capable of reconstructing missing structural information from 2D images and presenting it in 3D format. The generated images can be used to assess a wide range of pulmonary conditions, including inflammations, structural abnormalities, unusual masses, infections, and other respiratory issues.
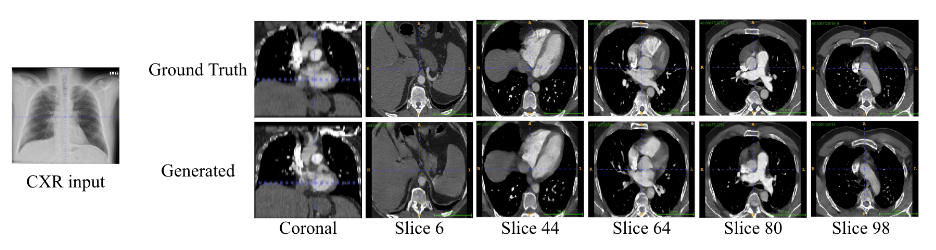
Initial results of the project indicate that the reconstructed images are highly accurate and capable of restoring critical structural information that is not visible in conventional radiographs. This method can serve as a complementary tool in medical imaging, paving the way for the development of innovative technologies in the diagnosis and analysis of pulmonary diseases. Furthermore, the approach can be extended to other areas of medical imaging, contributing to improved diagnostic accuracy, continuous patient monitoring, and more effective evaluation of treatment outcomes. The adoption of this technology across various medical fields has the potential to enhance image interpretation and support more informed clinical decision-making.


